Huge rise in the number of bariatric procedures in performed in Asia–Pacific region
- owenhaskins
- Jul 1, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Jul 4, 2022
The number of bariatric procedures performed in the Asia–Pacific Region have increased rapidly in the last decade increasing from 18,280 operations in 2010 to 66,010 in 2019, and falling to 49,553 in 2020, according to researchers writing on behalf of IFSO-APC. Specifically, the authors noted that "the rise in procedures is primarily due to the expansion of surgical criteria and establishment of public health insurance system based on the dedication of the IFSO and IFSO-APC members in each country and region." The findings were reported in the paper, ‘Ten Years of Change in Bariatric/Metabolic Surgery in the Asia–Pacific Region with COVID-19 Pandemic: IFSO-APC National Reports 2021’, published in Obesity Surgery.
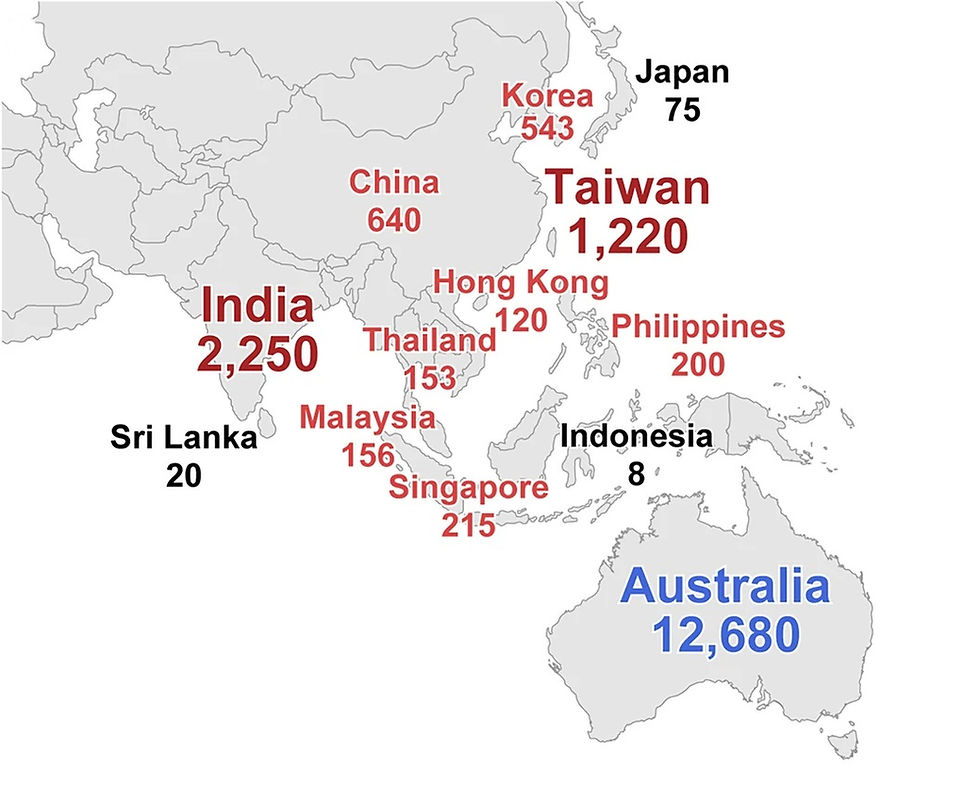
For the paper, the researchers collected national bariatric/metabolic surgery data from the 13 of 14 national societies using a questionnaire that consisted of ten general questions. In the 13 IFSO-APC countries and regions, there were 466 bariatric surgeons and 296 bariatric institutions in 2010, and 1,875 bariatric surgeons and 932 institutions in 2020; a 4.0-fold increase in the number of bariatric surgeons and a 3.1-fold increase in the number of institutions (both p=0.001).
In the IFSO-APC countries and regions, a total of 18,280 patients underwent bariatric/metabolic surgery in 2010, 66,010 in 2019 (p<0.001) and 49,553 in 2020 (p=0.032), a 3.6-fold increase and a 2.7-fold increase, respectively (Figure 1). The researchers noted that there was no significant difference in the total number between 2019 and 2020 (p=0.509). In Japan, China, and Malaysia, the number of cases in 2019 increased by more than tenfold compared to 2010.

In 2010, adjustable gastric banding (AGB) accounted for 54.2% of the procedures, sleeve gastrectomy (SG) accounted for 33.0% and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) accounted for 11.7%. However, in 2019, SG accounted for 67.0% of the procedures, one anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB) accounted for 13.5% and RYGB accounted for 12.1%. In the 2020 data (Indian data not included), SG accounted for 75.7% of the procedures, RYGB accounted for 9.1% and OAGB accounted for 5.5%.
Seven of the 13 countries (53.8%) reported that the biggest changes in the last decade were increased numbers of bariatric surgeons and institutions, seven countries (53.8%) also reported that there was an increased number of bariatric/metabolic cases and six countries (46.2%) noted a public insurance coverage of bariatric/metabolic surgery was established or expanded in the last decade.
The authors also reported that the average prevalence of obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) in the general population in 2010 and 2016 was 6.7% (2.8–25.6%) and 8.5% (3.7–29.0%), respectively, and the population of individuals with obesity significantly increased in all of the countries (p=0.001).
With regard to type 2 diabetes, the average prevalence in the general population in 2010 and 2021 was 7.6% (4.2–11.6%) and 9.8% (6.4–19.0%), respectively, and the population of individuals with T2DM significantly increased in ten of the 13 countries (76.9%) (p=0.014).
Further information
To access this paper, please click here



Comments